
链表是一种物理存储结构上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。
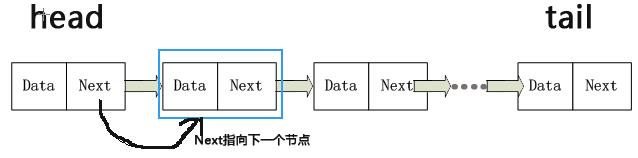
节点维护变量data和next,分别用于存储数据和指向下一个节点。
C#:
class Node<T>
{
private T data;
private Node<T> next;
public T Data
{
get { return data; }
set { data = value; }
}
public Node<T> Next
{
get { return next; }
set { next = value; }
}
public Node(T item)
{
data = item;
}
public Node(T item, Node<T> nextNode)
{
data = item;
next = nextNode;
}
}
Python:
class Node:
def __init__(self, data, next=None):
self.data = data
self.next = next
def __repr__(self):
return str(self.data)
正式构建一个链表类
链表类应该具有以下属性或方法:
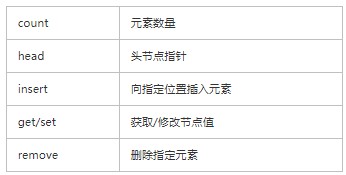
定义好一个类:
C#:
class LinkList<T>:
{
private Node<T> head;//头节点
private int count;//计数器
}
Python:
class LinkList:
def __init__(self):
self._head = None
self.count = 0
1.获取链表元素个数
由于我们维护了一个属性,所以直接返回count即可
class LinkList<T>:
{
...
public int Count { get { return count; } }
}
在Python中我们重写__len__方法
def __len__(self):
return self.count
2.获取指定位置节点
类比索引功能,设定头节点位置为0,下一节点位置+1
实现一个函数,返回指定位置的Node对象,两种直观解决思路:
迭代,通过一个while或循环来遍历至指定位置
递归,链表是一种天然适合递归的数据结构,通过递归也可以轻松找到目标节点
C#(迭代实现):
private Node<T> GetIndexNode(int index)
{
//获取指定索引的Node对象
if (index > count)
{
throw new IndexOutOfRangeException();
}
Node<T> target = head;
for (int i = 0; i < index; i++)
{
target = target.Next;
}
return target;
}
Python(递归实现):
def _getnode(self, index: int):
# 返回指定索引的节点
def getnode(node: Node, offset: int):
'''递归函数
:param node: 节点
:param offset: 偏移量
:return:
'''
if not node or offset < 0:
raise IndexError('超出索引范围')
if offset == 0:
return node
return getnode(node.next, offset-1)
return getnode(self._head, index)
Tips:使用递归实现可能会出现栈溢出,python默认调用栈容量1000
3.向指定位置插入一个节点
向位置i插入一个节点,只要找到目标位置前一个节点(i-1),把i-1节点的next指向新节点,再把新节点的next节点指向i+1节点即可
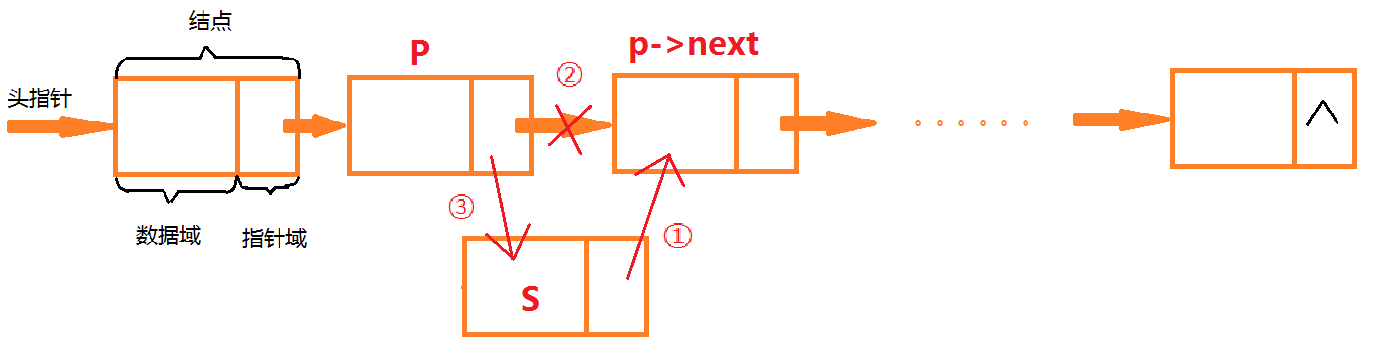
特别要注意如果向0位置插入节点,要修改head的指向
C#:
public void Insert(T item, int i)
{
if (i == 0)
{
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item,head);
head = newNode;
}
else
{
Node<T> preNode = GetIndexNode(i - 1);
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item, GetIndexNode(i));
preNode.Next = newNode;
}
count++;
}
Python:
def insert(self, item, index):
if index > self.size:
raise IndexError
if index == 0:
node = Node(item, self._head)
self._head = node
else:
prev = self._getnode(index - 1)
node = Node(item, prev.next)
prev.next = node
self.count += 1
4.访问/修改一个节点的值
前面已经实现了查找节点的访问,现在只用提供一个接口get/set节点存储的值即可
C#:
public T GetItem(int i) { return GetIndexNode.Data; }
Python:
def __getitem__(self, item):
if not isinstance(item,int):
raise IndexError
return self._getnode(item).data
def __setitem__(self, key, value):
if not isinstance(key,int):
raise IndexError
node = self._getnode(key)
node.data = value
实际上,我们实现的增删改查大多基于GetIndexNode方法,时间复杂度随元素的位置而定,如果操作在链表头,那么时间复杂度O(1),如果操作在链表尾,时间复杂度则O(n),整体来看增删改查的时间复杂度均为O(n)。
与数组对比,由于数组是一个在内存连续存放的数据结构,所以数组支持随机访问(任意索引访问时间复杂度均为O(1))。在随机读写性能上数组会比链表有更好的表现,但是链表也有优点,链表是一个实现了自动扩容的数据结构,我们完全可以不去关心一个链表能容纳多少元素,而数组则往往来通过扩容来实现动态数组,也会造成空间和时间的浪费。
实际上,链表一般只在尾部添加元素,我们完全可以再维护一个foot变量指向链表尾来优化效率。
动力节点在线课程涵盖零基础入门,高级进阶,在职提升三大主力内容,覆盖Java从入门到就业提升的全体系学习内容。全部Java视频教程免费观看,相关学习资料免费下载!对于火爆技术,每周一定时更新!如果想了解更多相关技术,可以到动力节点在线免费观看数据结构视频教程哦!
提枪策马乘胜追击04-21 20:01
代码小兵87207-15 12:10
杨晶珍05-11 14:54
杨晶珍05-12 17:30